Cisco ISE Interview Questions- If you are looking for a job related to the ISE administrator, you need to prepare for the latest Cisco ISE Interview Questions. Every interview is indeed different as per the various job profiles. Here, we have prepared the most important Interview Questions and Answers that will help you get success in your upcoming interview and help you get your dream job in your dream company.

Introduction to ISE
Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE) is a next-generation identity, access control, and policy platform that enables enterprises to enforce compliance, enhance infrastructure security, and streamline their service operations. The unique architecture of the Cisco ISE allows enterprises to gather real-time contextual information from networks, users, and devices.
The administrator can then use that information to make proactive governance decisions by tying identity to various network elements including access switches, wireless LAN controllers (WLCs), virtual private network (VPN) gateways, and data center switches. Cisco ISE is a key component of the Cisco Security Group Access Solution.
This guide on “Cisco ISE interview questions and answers” aims to equip you with essential knowledge and practical insights, helping you confidently tackle interview questions and secure a position as an ISE administrator.
Key Topics Covered:
- Basics of Cisco ISE: Understanding its core functions and architecture.
- Personas in ISE: Roles of Policy Administration Node (PAN), Monitoring Node (MnT), and Policy Services Node (PSN).
- Deployment Types: Standalone, Hybrid, and Distributed deployments.
- Licensing Models: Base, Plus, Apex, and Device Administration licenses.
- Key Features: Authentication, authorization, policy sets, and identity stores.
- Protocols and Security: Differences between TACACS and RADIUS, and the role of dot1x and MAB.
By mastering these areas, you’ll be well-prepared to answer a wide range of interview questions related to Cisco ISE and demonstrate your expertise effectively.
Q1. What is the Cisco ISE (Identity Services Engine)?
In simple terms, you can control who can access your network and when they do what they can get access to. It can authenticate wired, wireless, and VPN users and can scale to millions of endpoints.
Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE) is a network administration product that enables the creation and enforcement of security and access policies for endpoint devices connected to the company’s Network Administrator devices such as routers and switches. The purpose is to simplify identity management across diverse devices and applications.
Q2. What are the different types of personas on Cisco ISE?
- Policy Administration Node (PAN)
- Monitoring Node (MnT)
- Policy Services Node (PSN)
Depending on the size of your deployment all three personas can be run on the same device or spread across multiple devices for redundancy.
Q3. Explain the different types of personas on ISE?
Policy Administration Node (PAN) is where the administrator will login to configure policies and make changes to the entire ISE system. Once configured on the PAN the changes are pushed out to the policy services nodes. It handles all system-related configurations and can be configured as standalone, primary, or secondary.
Monitoring Node (MnT) is where all the logs are collected and where report generation occurs. Every event that occurs within the ISE topology is logged to the monitoring node you can then generate reports showing the current status of connected devices and unknown devices on your network.
Policy Services Node (PSN) is the contact point in the network. Each switch is configured to query a radius server to get the policy decision to apply to the network port the radius server is the PSN. In larger deployments, you use multiple PSN’s to spread the load of all the network requests. The PSN provides network access, posture, guest access, client provisioning, and profiling services. There must be at least one PSN in a distributed setup.
Q4. How can we deploy ISE?
ISE can be either deployed on a physical appliance or a Virtual Machine that enables the creation and enforcement of access policies for endpoint devices connected to a company’s network.
Physical appliance: Cisco SNS-3715, Cisco SNS-3755, Cisco SNS-3795
Virtual: ISE can be installed on VMware, Hyper-V
Q5. What is the main objective of Cisco ISE?
Every time a wired or wireless user wants to access the network or tries to access a device [for device administration], the user is validated against the server to check if he/she is permitted to do so. Depending on the end result, the user will be allowed certain access to network/device.
Q6. What is the difference between Cisco ISE vs ACS?
ACS is used to authenticate users to network devices and for VPN sessions but it is not a NAC solution wherein it will not be able to control the network by checking the compliance state of the devices in the network.
ISE is the next generation of network authentication and is so much more powerful than ACS. If you want to implement full network access control you need ISE.
Q7. What are the different types of deployments in ISE?
ISE has three different deployment options.
- Standalone
- Hybrid deployment
- Distributed deployment
Q8. Briefly explain different types of ISE deployment.
Standalone Deployment: A deployment that has a single Cisco ISE node is called a standalone deployment. This node runs the Administration, Policy Service, and Monitoring personas. This deployment is suitable for Small production setups or labs. If we are deploying ISE in standalone mode then we will not have redundancy.
Hybrid Deployment: A deployment that has multiple ISE nodes wherein PAN and MNT will be on enabled on a single node. This node will run PAN and MNT along with this we ca dedicated PSN’s in the deployment.
Distributed Deployment: A deployment that has multiple ISE nodes wherein we have a separate node for each persona. The distributed deployment consists of one Primary Administration ISE node, Secondary admin nodes, Primary Monitoring node, and Secondary Monitoring node followed by PSN(Policy Service Node).
Each node can perform one or multiple services. ISE implementation is typically deployed in a distributed manner with individual services run on dedicated ISE nodes.
Q9. Explain the various types of ISE Distributed deployment.
ISE distributed model can be deployed in 3 different ways depending on the scale.
- Small Network Deployments
- Medium Network Deployments
- Large Network Deployments
Small Network Deployments: A typical small ISE deployment consists of two Cisco ISE nodes with each node running all 3 services on it. The primary node provides all the configuration, authentication and policy functions and the secondary node functions as a backup.
The secondary supports the primary in the event of a loss of connectivity between the network devices and the primary. In case if the primary ISE node goes down we need to manually promote Secondary to Primary.
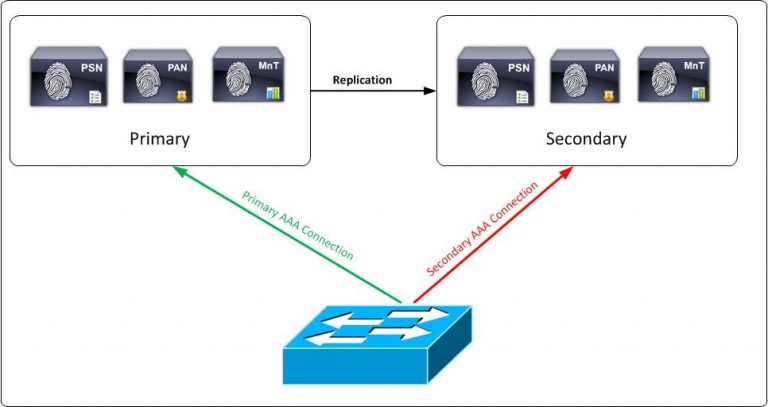
Medium Network Deployment: The medium-sized deployment consists of a primary and secondary administration node and a primary and secondary monitoring node, alongside separate policy service nodes. Here in this deployment PAN and SAN will take care of the administration and log collection part wherein PSN’s will handle authentication for both radius and Tacacs traffic.
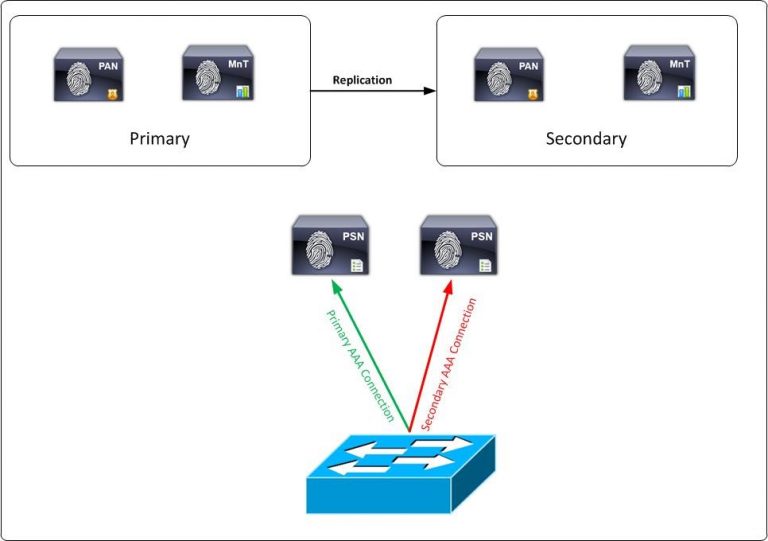
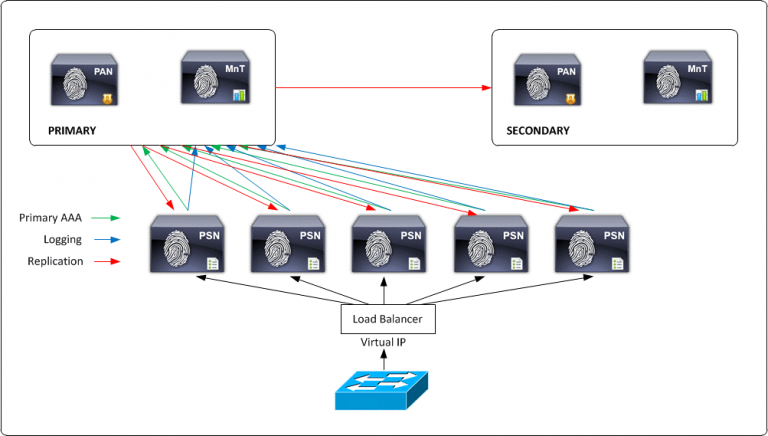
Large Network Deployment: ISE can distribute large individual ISE personas among several ISE nodes with a large network deployment you dedicate each node to a separate persona. So a separate node (secure network server) for administration, monitoring, and policy service. You should also consider using load balancers in front of the PSN nodes.
Having a single load balancer does introduce a potential single point of failure so it is highly recommended to deploy two load balancers. Since it’s a large network deployment we can have multiple logging servers so that logs can be transferred across each server.
Q10. What are all the different types of Licenses that we can have on ISE?
- ISE Essential
- ISE Advantage
- ISE Premier
for detailed information follow Cisco ise licensing page
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/security/identity-services-engine/ise-licensing-guide-og.html
Q11. What are the different types of Licenses?
Cisco ISE offers various licensing options to cater to different deployment needs:
- Subscription Licenses:
- Essentials: Basic identity and access management, guest access, and posture assessment.
- Advantage: Adds profiling, BYOD, pxGrid integration, and TrustSec Security Group Tagging (SGT).
- Premier: Comprehensive features including endpoint compliance, security automation, and advanced threat containment.
- Device Admin Licenses: For TACACS+ services on a Policy Service Node.
- Virtual Machine Licenses: Applicable for deploying ISE on non-Cisco hardware or virtual environments.
Licensing is managed through Cisco’s Smart Software Manager, simplifying activation and management. Licenses are categorized by the number of active endpoints and can be purchased in 1-, 3-, or 5-year terms.
For detailed information, refer to the Cisco ISE Licensing Guide.
Evaluation: An evaluation license covers 100 nodes and provides full Cisco ISE functionality for 90 days. All Cisco ISE appliances are supplied with an evaluation license. Evaluation licenses will collectively have a base, plus, apex, device administration and so on for 90 days.
Q12. Does Cisco ISE support Tacacs?
Cisco ISE supports device administration using the TACACS+ security protocol to control and audit the configuration of network devices. The network devices are configured to query ISE for authentication and authorization of device administrator actions and send accounting messages for ISE to log the actions.
Cisco ISE now supports TACACS+. Prior to ISE 2.0 ISE was only supporting Radius but post 2.0 ISE versions TACACS is supported.
Device admin is not enabled by default, to enable it go to:
Administration / Deployment / Node Name / Enable Device Admin Service
This service should be enabled on the PSNs.
Q13. What are the different types of protocols that are supported on ISE?
There are different protocols available on ISE which is used for authenticating and authorizing end clients. Below mentioned are the few known and popularly used protocols.
EAP-TLS, PEAP, MS-CHAPv2 v1 and v2, EAP-TTLS, EAP-MS-CHAPv2, LEAP, EAP FAST.
Q14. What are policy sets on ISE?
Cisco ISE is a policy-based, network-access-control solution, which offers network access policy sets, allowing you to manage several different network access use cases such as wireless, wired, guest, and client provisioning.
When you install ISE, there is always one policy set defined, which is the default policy set, and the default policy set contains within it, predefined and default authentication, authorization and exception policy rules.
Q15. What is the major difference between Authentication and Authorization conditions on ISE?
Authentication: In Authentication, we will check if the user is present in the identity store or not and the credentials which are presented by the user are valid or not. For example, a standard Authentication policy can include the type of traffic i.e. if the user traffic wired or wireless and which is the identity store which needs to be checked upon for this traffic.
Authorization: In Authz we fetch different attributes for the user and determine for which resources the user has access to. An authorization policy can consist of a single condition or a set of conditions that are user-defined. These rules act to create a specific policy. For example, a standard policy can include the rule name using an If-Then convention that links a value entered for identity groups with specific conditions or attributes to produce a specific set of permissions that create a unique authorization profile.
Q16. What is Identity Store on Cisco ISE?
Identity Store is where we check for the credentials against a particular database. Identity store database can be internal or external. Internal identity store will refer to Identity/Endpoint information which is created locally on ISE. External identity store can be AD, LDAP, Radius token server, RSA and Certificate Authority.
Q17. What is the difference between Tacacs and Radius?
TACACS: Terminal Access Controller Access Control System (TACACS+) is a Cisco proprietary protocol which is used for the communication of the Cisco client and Cisco ACS server. It uses TCP port number 49 which makes it reliable.
RADIUS: Remote Access Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) is an open standard protocol used for the communication between any vendor AAA client and ACS/ISE server. The standard ports used for radius communication are 1812 for authentication and 1813 for accounting. Legacy radius port number are 1645 for authentication and 1646 for accounting.
| RADIUS | TACACS |
| RADIUS uses UDP 1812 for Auth and 1813 for Accounting(Legacy ports:1645,1646) | TACACS uses TCP port no 49 |
| RADIUS combines Authentication and Authorization | TACACS treats Authentication, Authorization and Accounting separately |
| RADIUS is an open protocol supported by multiple vendors | TACACS is Cisco proprietary |
| Primary us of Radius is Network Access | The primary use of TACACS is Device Administration |
| Encrypts only the Password field | Encrypts the entire Payload |
Q18. What is dot1x?
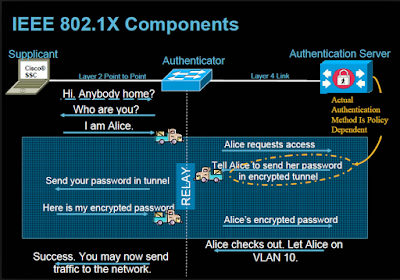
802.1X defines a client-server-based access control and authentication protocol that restricts unauthorized clients from connecting to a LAN through publicly accessible ports. Until and unless the post is not authorized, the access will not be given to the end client who’s connecting on that port.
Until the client is authenticated, 802.1X access control allows only Extensible Authentication Protocol over LAN (EAPOL) traffic through the port to which the client is connected. After authentication is successful, normal traffic can pass through the port.
Q19. What is Mac Authentication Bypass(MAB)?
MAC Authentication Bypass (MAB) is a way to give a white-list to certain network devices. If you know the MAC address of a certain device you know should get access to your network you can grant it access purely by its MAC address. This is used for devices that cannot have certificates loaded on them or are hard to profile. In MAB username and password both will be the MAC address.
Before MAB authentication, the identity of the endpoint is unknown and all traffic is blocked. The switch examines a single packet to learn and authenticate the source MAC address. After MAB succeeds, the identity of the endpoint is known and all traffic from that endpoint is allowed.
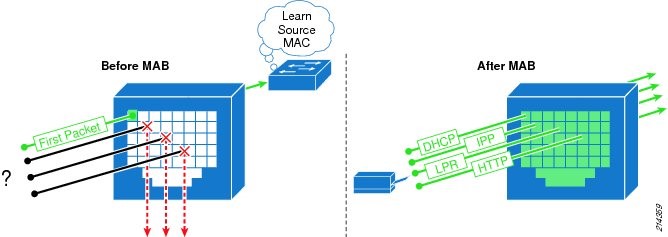
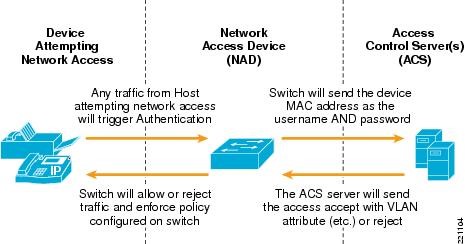
Q20. What are the key components involved in dot1x and MAB authentication?
Supplicant, Network Access Device, and Authentication Server are the 3 key components that are involved in dot1x authentication.
Supplicant: User/Endpoint who’s trying to authenticate in order to gain network access.
NAD: Access switch/Access point to which the supplicant is connected which will carry the user credentials and present it to the server in order to authenticate the user.
Authentication Server: Credentials that were presented by NAD will be verified on the server and depending on the end result either access will be given or denied.
Q21. What is Profiling in Cisco ISE?
The Profiling service in Cisco Identity Services Engine Identifies the devices that connect to your network and their location. Later the endpoints are profiled based on the endpoint policies configured in Cisco ISE. The profiling service allows the identity services engine to profile devices connected to the network and give them an identity based on numerous factors. These devices can then be granted access or denied access to the network based on the security policies which are defined on ISE.
Q22. What is the use of profiling in Cisco ISE?
Cisco ISE Profiling Services provides dynamic detection and classification of endpoints connected to the network. Using MAC addresses as the unique identifier, ISE collects various attributes for each network endpoint to build an internal endpoint database. In this case instead of adding endpoints manually on the identity groups with help of profiling service devices can be detected dynamically and based on policy sets which have been configured access can be given accordingly.
Q23. How do you enable Profiling on Cisco ISE?
The ISE Profiling feature set requires the installation of a Plus license on the Policy Administration Node (PAN). One Plus feature license is required for each endpoint that is actively authenticated to the network and where profiling data is used to make an Authorization Policy decision.
Profiling has to be enabled from the Administration .>Deployment > Enable Profiling Service on whichever PSN which you wish to handle the Profiling traffic.
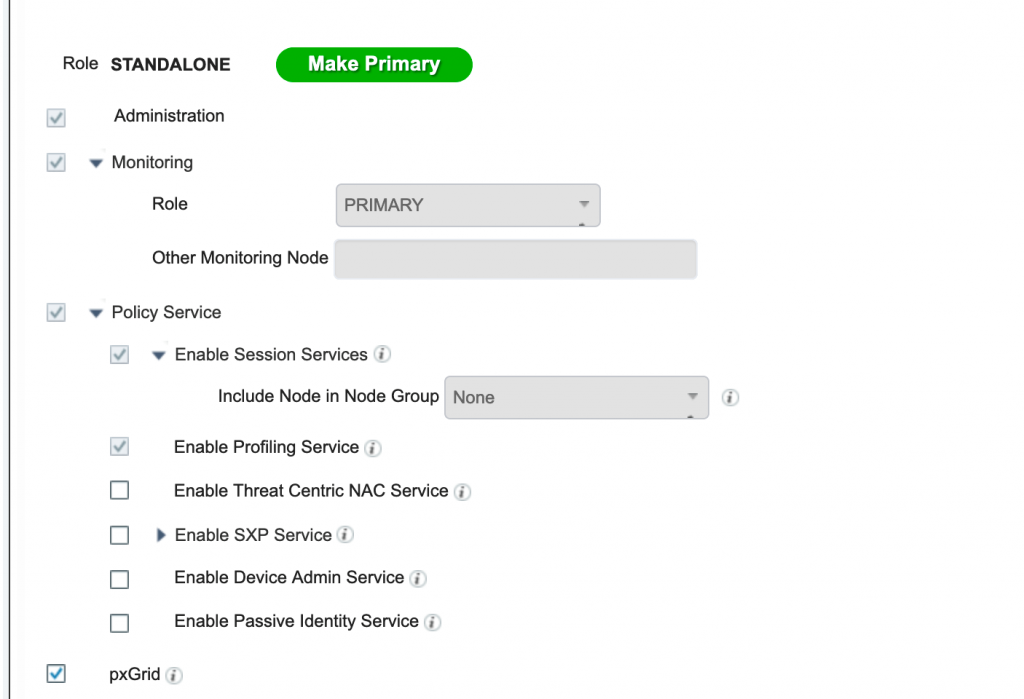
Q24. How do you deploy profiling in the production deployment?
A typical network deployment would start by putting ISE into monitor mode. In monitor mode no enforcement takes place but the ISE administrator can start to see what devices are connecting to the network and what identity it has been given. During this phase, a lot of devices are normally discovered that the network administrator did not even know were connected to the network.
Based on the devices which are connecting in the network and the profiles which are being assigned network administrator can tweak in case if he/she needs the precise profiling groups or create new profiling policies. With this approach of Profiling deployment Network Administrator will have a complete picture of all devices that are connected to your network and will be in complete control of their access.
Q25. What is Device Sensor?
Device Sensor feature is used to gather raw endpoint data from network devices using protocols such as Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP), Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP), and DHCP. The endpoint data is made available to registered clients in the context of an access session.
Q26. What are Probes and which are the various types of probes used in Cisco ISE?
A probe is a method used to collect an attribute or a set of attributes from an endpoint on your network. The probe allows you to create or update endpoints with their matched profile in the Cisco ISE database. ISE Profiling Services uses various collectors, or probes, to collect attributes about connected endpoints.
Probes help you to gain more network visibility. Below mentioned are the commonly used probes in Cisco ISE.
- RADIUS Probe
- DHCP Probe
- NAMP Probe
- SNMP Probe
- HTTP Probe
- HTTP SPAN Probe
- NetFlow Probe
- Active Directory Probe
Probes can be enabled from Administration > Deployment > Profiling Configuration and enable the required probes as per your network.
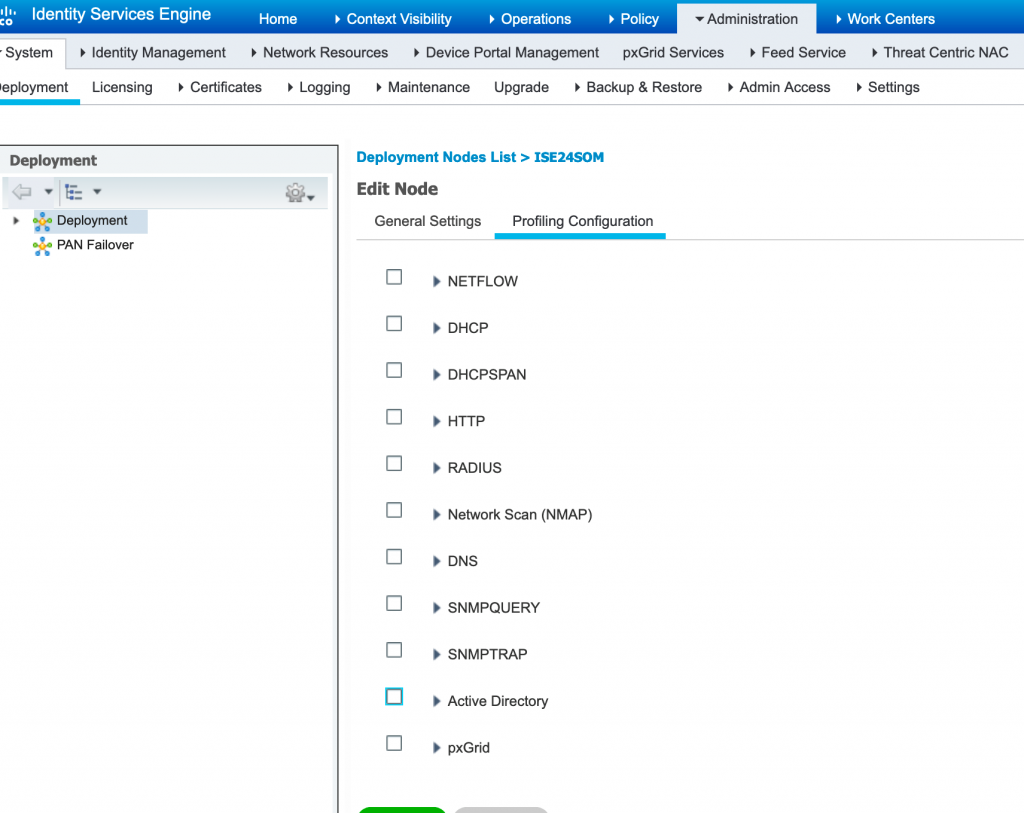
Q27. What is Profiling Feed Service and what is the use of it?
Profiling Feed Service is the database which has information about profiling policies and the updated OUI and this database can be downloaded from a designated Cisco feed server through a subscription into Cisco ISE.
By updating the Profiling Feed latest Database can be downloaded which will have the updated Profiling policies and OUI’s. We can even configure to receive e-mail notifications to the e-mail address as an administrator of Cisco ISE that you have configured for applied, success, and failure messages.
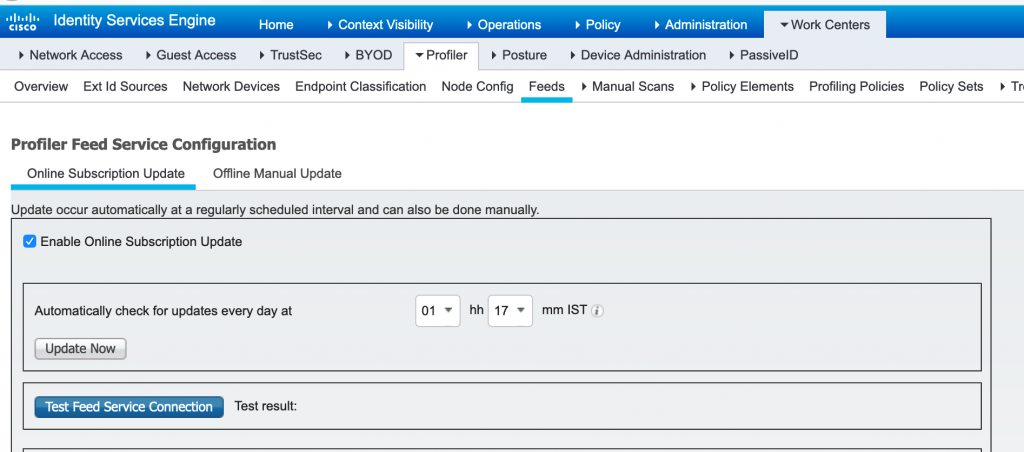
Profiling feed will be updated only when Cisco provided profiling policies and the endpoint profiling policies which were modified by the previous update, are updated. Profiling Feed can be updated offline as well by downloading from cisco site with CCO credentials and uploading it manually to Cisco ISE.
Q28. What is Posture service in Cisco ISE?
Posture is a service in Cisco Identity Services Engine (Cisco ISE) that allows you to check the state, also known as posture, of all the endpoints that are connecting to a network for compliance with corporate security policies. This allows you to control clients to access protected areas of a network.
Q29. Which type of License is required to host Guest portals in Cisco ISE?
Cisco ISE Posture requires the installation of an Apex license. If you have not installed the Apex license on the Primary PAN, then the posture requests will not be served in Cisco ISE.
Q30. What are the various endpoint Compliance posture states?
The compliance (posture) status of an endpoint can be:
Unknown: No data was collected in order to determine the posture state.
Non-Compliant: A posture assessment was performed, and one or more requirements failed.
Compliant: The endpoint is compliant with all mandatory requirements.
Q31. What are the various probes which are initiated during policy server detection?
There is a series of probes which will be sent during policy server detection.
Default Gateway IP
Discovery Host
Previously connected PSN over SSL on port 8905
Default Gateway: In this state discovery of the policy server detection will be attempted to the default gateway.
Enroll.cisco.com : If there is no response received from the default gateway then discovery will be attempted on enrol.cisco.com. This FQDN needs to be successfully resolvable by DNS server.
Discovery Host : Here http get request will be sent in order to find policy server to discovery host. Discovery host value is returned from ISE during installation in AC posture profile. Expected result for the probe is redirect-URL.
Previously connected PSN: Here http get request will be sent across to previously connected PSN on port 8905. This request contains information about client IPs and MACs list for session lookup on ISE side. This probe is not presented during the first posture attempt. Connection is protected by ISE admin certificate. As a result of this probe ISE can return session ID back to the client if node where probe landed is the same node where user has been authenticated.
Q32. Name a few compliance conditions check which can be done Cisco ISE using Posture?
The posture policy defines the set of requirements for an endpoint to be categorised as compliant based upon file presence, registry key, process, application, Windows, and anti-virus (AV)/anti-spyware (AS) checks and rules. Posture policy is applied to endpoints based upon a defined set of conditions such as user identity and client OS type.
Q33. What is Cisco TrustSec?
Cisco TrustSec is an embedded technology in your existing Cisco infrastructure. TrustSec can simplify provisioning and management of network access, make security operations more efficient, and help to enforce segmentation policy consistently, anywhere in the network.
Cisco TrustSec technology uses software-defined segmentation to simplify the provisioning of network access, accelerate security operations, and consistently enforce policy anywhere in the network. Cisco TrustSec is embedded technology in Cisco switches, routers, and wireless and security devices.
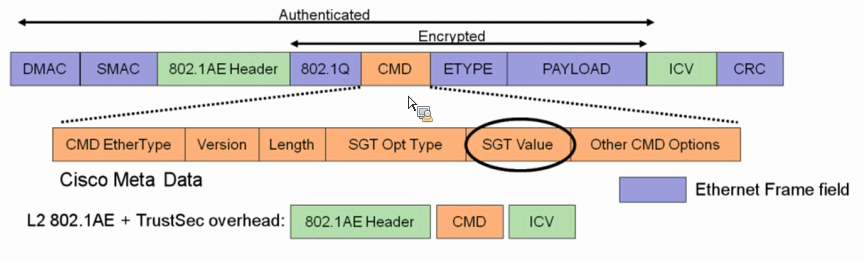
Q34. What is Secure Group Tagging in Cisco TrustSec?
The Security Group Tag (SGT) Exchange Protocol (SXP) is one of several protocols that supports Cisco TrustSec. CTS-SGT is a control protocol for propagating IP-to-SGT binding information across network devices that do not have the capability to tag packets.
Q35. What is pxGrid?
Cisco pxGrid (Platform Exchange Grid), your multiple security products can now share data and work together. This open, scalable, and IETF standards-driven platform helps you automate security to get answers and contain threats faster.
Cisco pxGrid is an open and scalable Security Product Integration Framework (SPIF) that allows for bi-directional any-to-any partner platform integrations. Cisco pxGrid uses a pub/sub model and publishes Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE) contextual information. In addition, pxGrid publishes this session directory topic and other ISE topics of information for ecosystem partners to consume.
Q36. What are the devices that can be integrated through pxGrid?
By using Cisco pxGrid we can integrate multiple security products in order to exchange information and work together. Below mentioned are the sample Firepower Management Center and Stealthwatch Management Center integration with ISE and benefits of it.
ISE and FMC can be integrated with pxGrid in order to exchange below mentioned information.
User to IP information will be provided by ISE to FMC through pxGrid.
SGT mapping information will be shared across to FMC from ISE via pxGrid.
With the help of pxGrid, we should be able to fetch information such as application info, information through NetFlow, threat data, firewall logs, MDM logs from multiple security products.
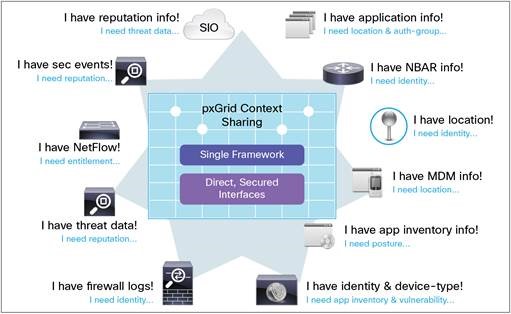
We can integrate Stealthwatch Management Console to ISE through pxGrid which will provide the Stealthwatch system with extra contextual information about the endpoint and user on that endpoint as well as the ability to quarantine that endpoint if they are misbehaving.
Q37. What is Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) and why is being used?
In BYOD employees are allowed to connect their personal devices securely to the network.
Employees are increasingly using both personal and work devices at their office and they don’t want to switch or carry both work and personal devices. They are willing to access their personal devices to access work application.
BYOD is a process wherein we onboard employees personal devices into the corporate network and provide access to the work applications from their own devices. By achieving this BYOD will simplify IT operations, providing “work-your-way” experience to employees, helping secure data by applying policies and controls.
Q38. What are the different design approach for BYOD solution in a wireless environment?
There are 2 design approach for implementing a BYOD solution in a wireless environment.
Single SSID solution.
Dual SSID Solution.
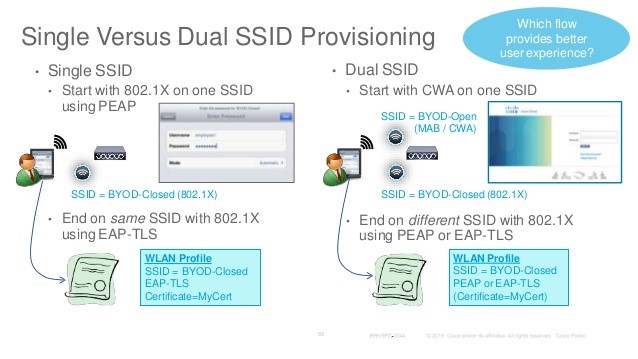
Q39. What is a Single SSID and Dual SSID solution in BYOD?
Single SSID :
In single SSID setup, same WLAN is used for certificate enrolment, provisioning(entire on-boarding process) and secure network access will be done on single SSID.
Dual SSID :
In Dual SSID setup, two SSID’s will be used wherein one SSID provides certificate enrolment and provisioning(entire on-boarding process) and the other SSID provides secure network access.
Q40. Explain the sample Single SSID and Dual SSID BYOD flow?
Single SSID Flow:
- User connects to secure SSID.
- PEAP: User enter username and password.
- User will be redirected to provisioning portal.
- User registers the personal device.
- Downloads certificate and supplicant configuration.
- User reconnects using EAP-TLS.
Dual SSID Flow:
- User connects to open SSID.
- User will be redirected to WebAuth portal.
- User enters guest or employee credentials.
- Guest signs AUP and guest access will be provided.
- Employee registers the device.
- Downloads certificate and supplicant configuration.
- Employee reconnects using EAP-TLS.
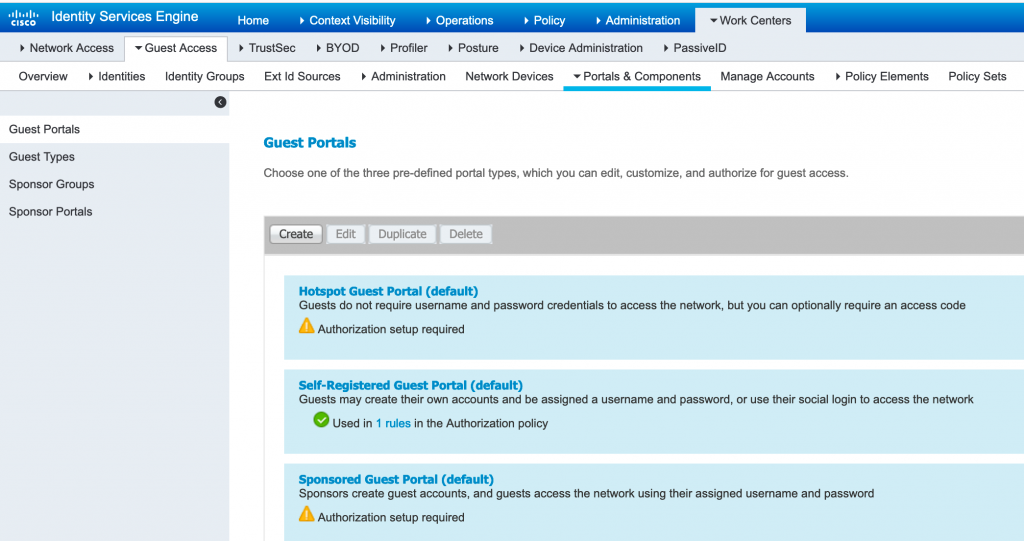
Q41. What are the various types of Guest portals in Cisco ISE?
There are 3 types of Guest portals:
- Sponsored Guest Portal
- Self-Registered Guest Portal
- Hotspot Guest Portal
Q42. What type of License is required to host Guest portals in Cisco ISE?
The ISE Guest feature set requires the installation of a Base license.
Q43. What are various types of Guests portal?
Sponsored Guest Portal:
Using the Sponsor portal, sponsors can create and manage temporary accounts for authorized visitors to securely access the corporate network or the Internet. After creating a guest account, sponsors also can use the Sponsor portal to provide account details to the guest by printing, emailing, or texting. Before providing self-registering guests access to the company network, sponsors may be requested via email to approve their guests’ accounts.
Self-Registered Guest Portal:
In Self-Registered portal, Guests will create their own accounts by registering themselves on the Self-Registered Guest portal. Based on the portal configuration, these self-registering guests may need sponsor approval before they receive their login credentials or they can log in post registering themselves on portal.
Hotspot Guest Portal:
The Hotspot Guest portal is an alternative Guest portal that allows you to provide network access without requiring guests to have usernames and passwords and alleviates the need to manage guest accounts. Instead, Cisco ISE works together with the network access device (NAD) and Device Registration Web Authentication (Device Registration WebAuth) to grant network access directly to the guest devices.
In order to create Guest portal navigate to WorkCentre >Portal & Components and create required Guest portal:
Note: Advanced interview questions on ISE are coming soon.
Understanding the intricacies of Cisco ISE is crucial for anyone preparing for a role as an ISE administrator. This comprehensive guide on “Cisco ISE interview questions and answers” covers the essential concepts, including different personas, deployment types, and licensing models, ensuring you’re well-prepared for your interview. By mastering these topics, you’ll be able to effectively manage identity, access control, and policy enforcement in any enterprise environment, positioning yourself as a strong candidate for your dream job.