DHCP (Dynamic Host Control Protocol)
In networks with a large number of hosts, statically assigning IP addresses and other IP information quickly becomes impractical.
Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP) provides administrators with a mechanism to dynamically allocate IP addresses, gateway and DNS rather than manually setting the address on each device.
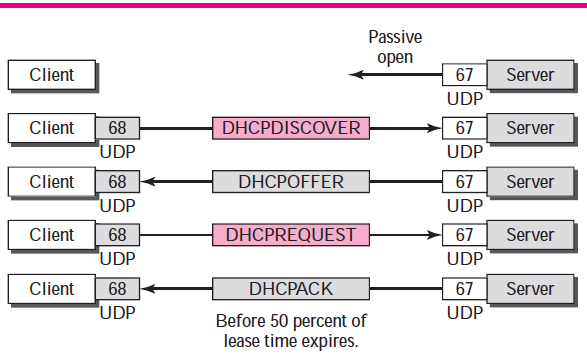
DHCP servers lease out IP addresses to DHCP clients, for a specific period of time. There are four steps to this DHCP process:
- When a DHCP client first boots up, it broadcasts a DHCPDiscover message, searching for a DHCP server.
- If a DHCP server exists on the local segment, it will respond with a DHCPOffer, containing the “offered” IP address, subnet mask, etc.
- Once the client receives the offer, it will respond with a DHCPRequest, indicating that it will accept the offered protocol information.
- Finally, the server responds with a DHCPACK, acknowledging the clients acceptance of offered protocol information.
DHCP Port – The server uses the well-known port 67, and The client uses the well-known port 68.
By default, DHCP leases an address for 8 days. Once 50% of the lease expires, the client will try to renew the lease with the same DHCP server. If successful, the client receives a new 8 day lease. However, if that IP address’s lease expires, you’ll be assigned a new IP address using the same DHCP protocols.
If the renewal is not successful, the client will continue “attempting” to renew, until 87.5% of the lease has expired. Once this threshold has been reached, the client will attempt to find another DHCP server to bind to.
In addition to IP address and subnet mask information, DHCP can provide the following protocol parameters:
- Default Gateway
- Domain Name and DNS servers
- Time Servers
- WINS servers
These are just a few examples of the many DHCP “options” that exist
What is Domain Name System (DNS)?
What is the Difference between DNS and DHCP?